Object storage is becoming the de facto standard for data movement and management of long-term storage. Commonly used in cloud storage, popular object storage solutions include Amazon S3, offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure Blob Storage and Google Cloud Storage. As data workflows become increasingly distributed, object storage is the more efficient way to manage data over time.
Defining Object Storage
Object storage is a type of data storage architecture that is designed to store and retrieve large amounts of unstructured data, such as video and audio files, documents, and images. Unlike traditional file storage systems, which use a hierarchical file system and are optimized for small numbers of large files, object storage systems are optimized for large numbers of small files. The metadata enables applications and users to browse and see what is available without actually touching the data. Object storage de-couples the valuable information about the data from the actual data itself, typically storing this information as metadata in a separate faster tier. This means it is much easier (and faster) to search through an unfathomable amount of data within an object storage system than a file-based system. Finally, an object-based system’s ability to automatically store multiple copies of data over a distributed system makes it easy to manage costs and enables extremely high data reliability.
Key Benefits
One of the key features of object storage is that it is highly scalable. Because the data is stored as objects rather than in a hierarchical file system, it can easily be spread across a large number of storage devices. This makes it possible to scale storage capacity as needed by adding more devices, rather than having to replace existing hardware. Due to the scalable nature of object storage, it is also majorly cost-efficient.
Another important feature of object storage is that it is designed to be highly durable. Data is typically spread across multiple devices to ensure that it is protected against the failure of any single device. Additionally, object storage systems often use erasure coding or other techniques to provide additional protection against data loss. To access the data in an object storage system, the client uses a simple API that allows it to create, read, update, and delete objects. The objects are typically accessed via a unique identifier, such as a URL, rather than by navigating a hierarchical file system. This makes it easy to integrate object storage into a wide variety of applications and services. One of the advantages of object storage is that it can be accessed from anywhere, by any device that can communicate with the object storage system over the internet. This makes it ideal for use cases such as cloud-based backup and archiving, large-scale data analytics, and content distribution. However, object storage is not suitable for use cases that require low-latency access to small numbers of large files. For example, it is not well suited for use cases such as databases or transactional systems, which require fast access to small numbers of highly structured data.
In conclusion, object storage is a cost-effective, highly scalable and durable data storage architecture. It is designed to store and retrieve large amounts of unstructured data, and its scalability and durability also makes it ideal for big data workloads. Intelligent object storage platforms can automatically move data based on storage policies which reflect the “value” of the storage tier in which it resides and the amount of total time since it was last used. When a user or application needs to retrieve a specific object, the unique object ID allows them to seamlessly retrieve the file, none the wiser as to which storage tier it was last located in. As data-driven organizations consider cloud storage, they should keep in mind the benefits of extending the infrastructure of the cloud (http and object storage) to local data centers to truly modernize on-premises, long-term data storage.
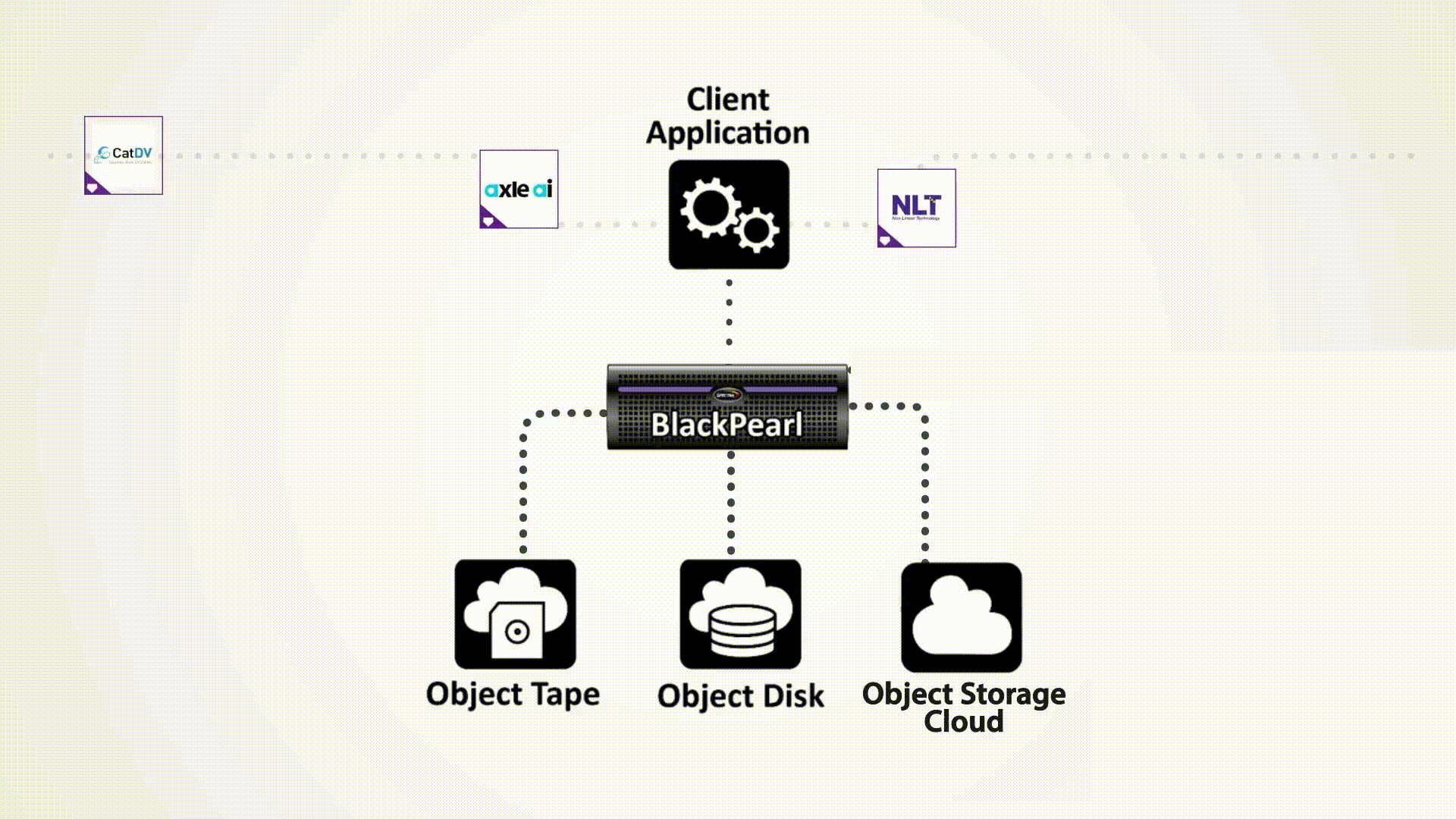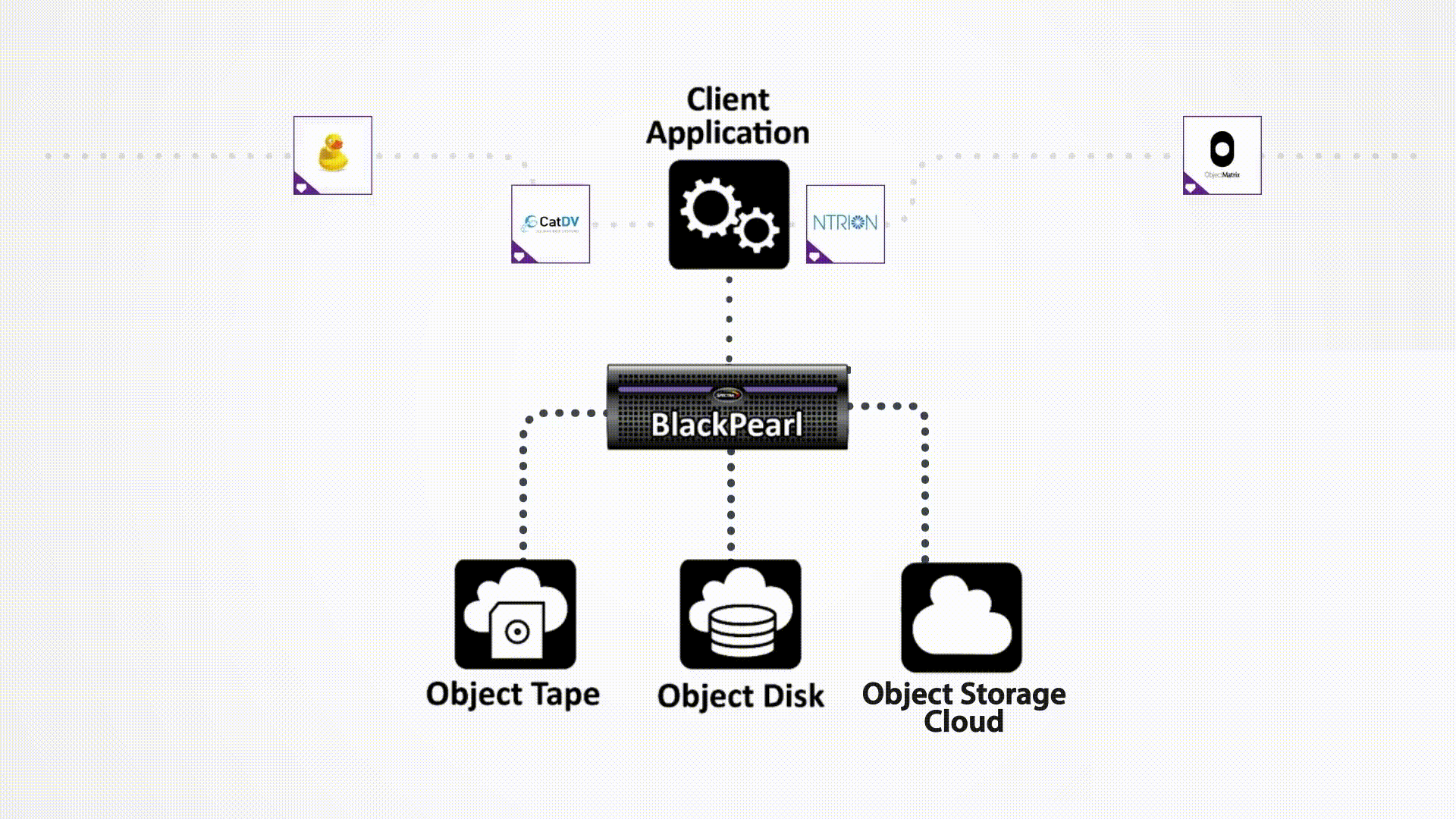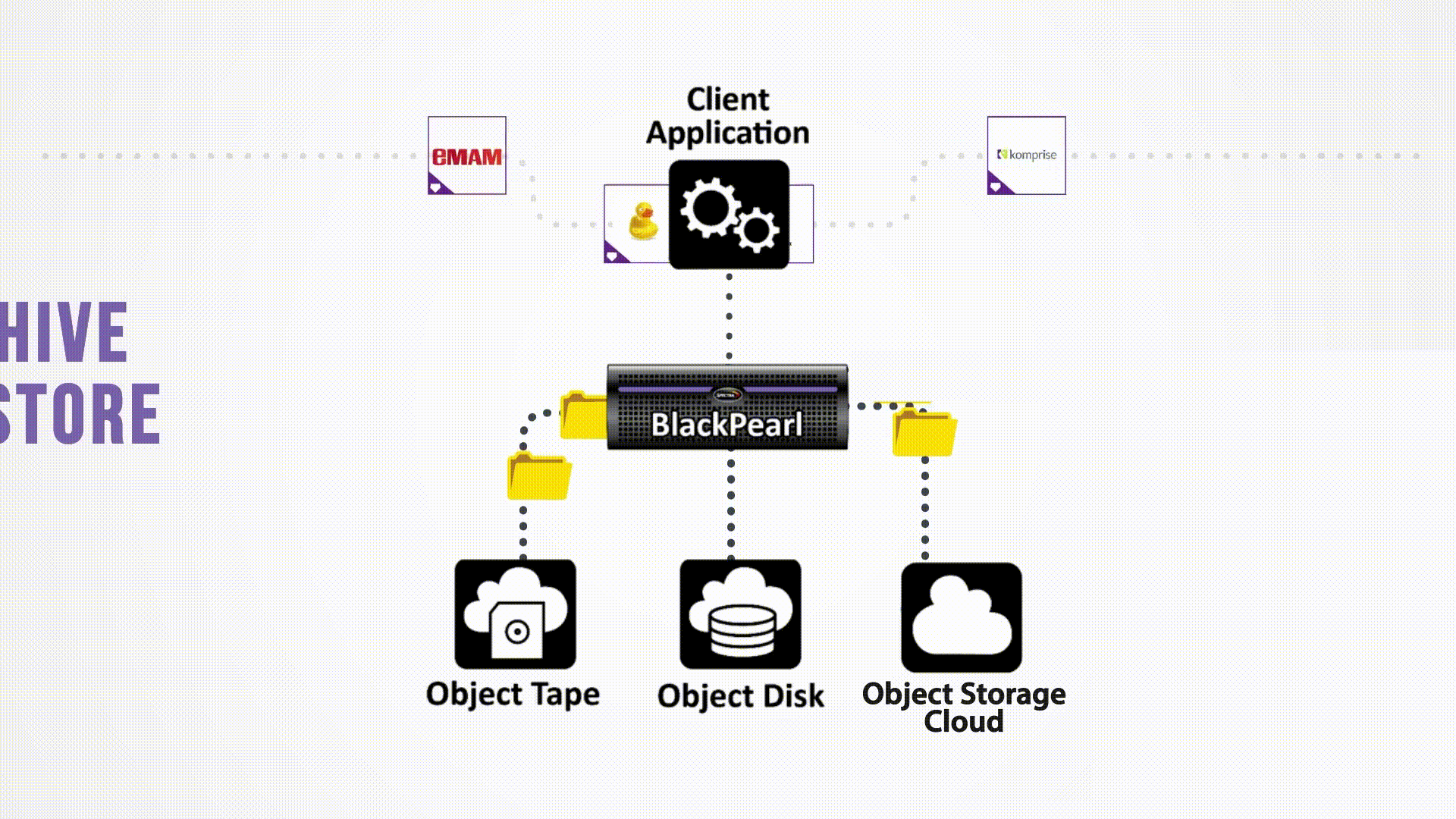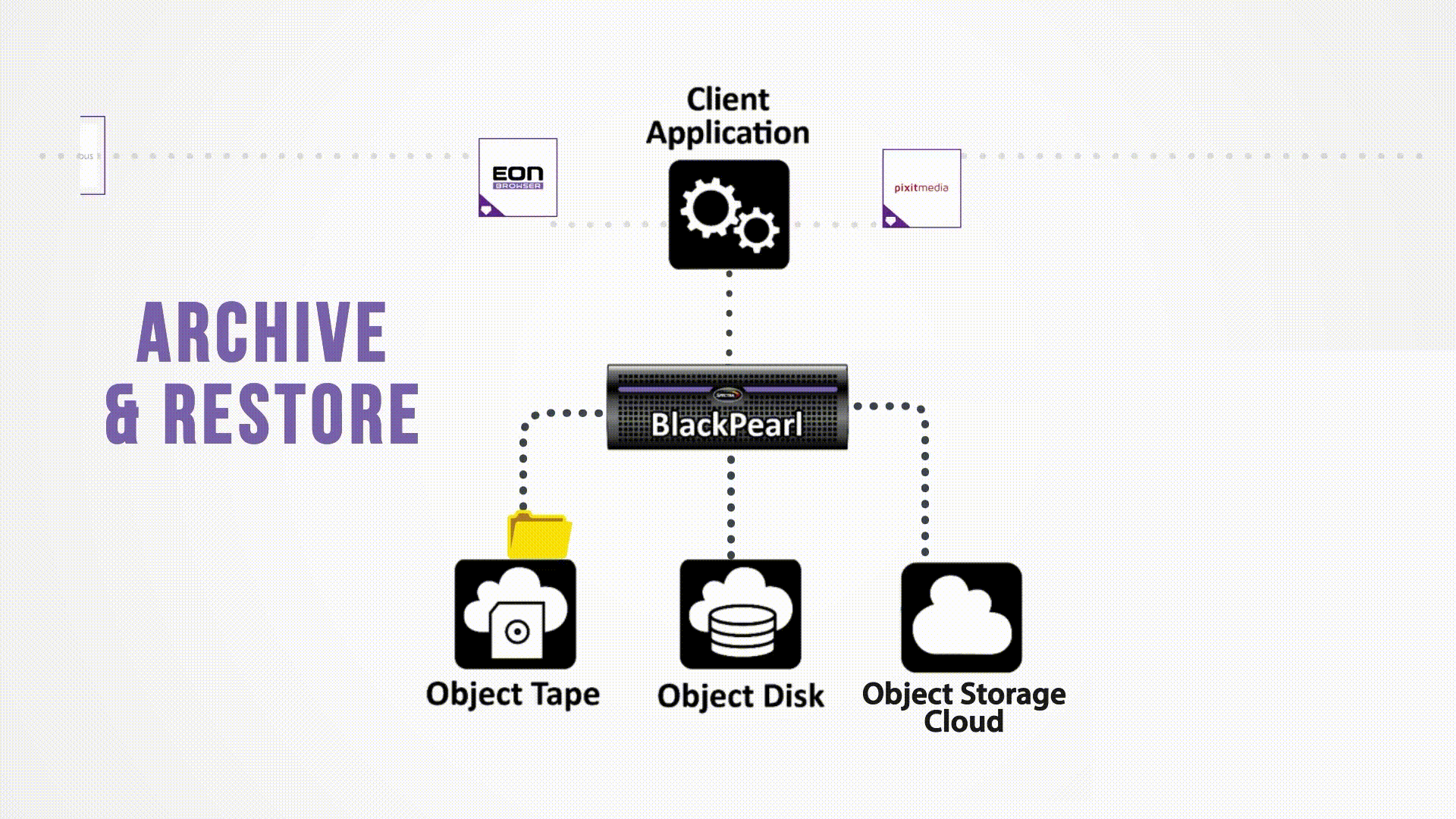
Bringing Object Storage Capabilities to Hybrid Cloud Architectures
Spectra’s BlackPearl Platform is based on a flexible, scalable architecture that can manage disk, tape, and cloud storage across multiple sites. The BlackPearl Platform delivers multi-purpose hybrid storage, combining software and hardware to create an end-to-end solution that enables organizations to leverage object storage to meet many business objectives. Integrated with a range of certified clients and file movers, BlackPearl easily and cost effectively scales up; adapts as operational requirements change; and enables easy synchronization of data between on-prem and cloud storage.
Learn more about BlackPearl here.